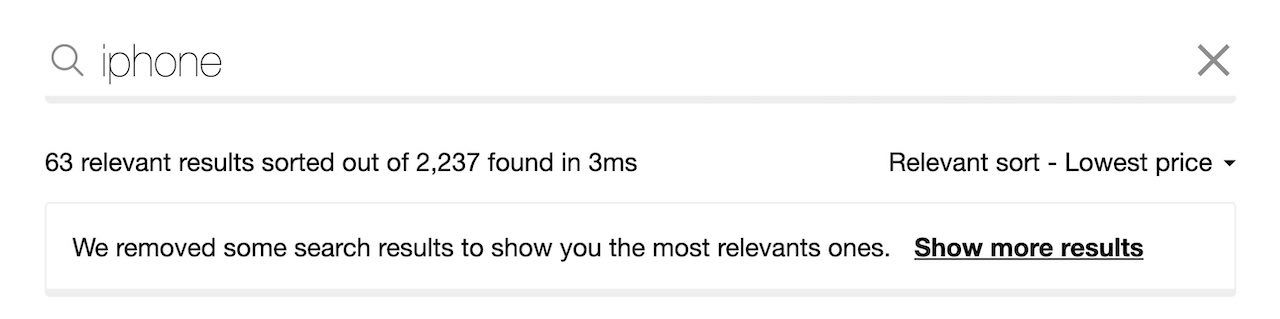
Relevant sorting
On this page
Use relevant sorting to only show the most relevant results for a user’s search instead of displaying all the records (exhaustive sorting).
Relevant sorting is available on the Build and Premium pricing plans.
Examples
These examples illustrate the difference between exhaustive and relevant sorting.
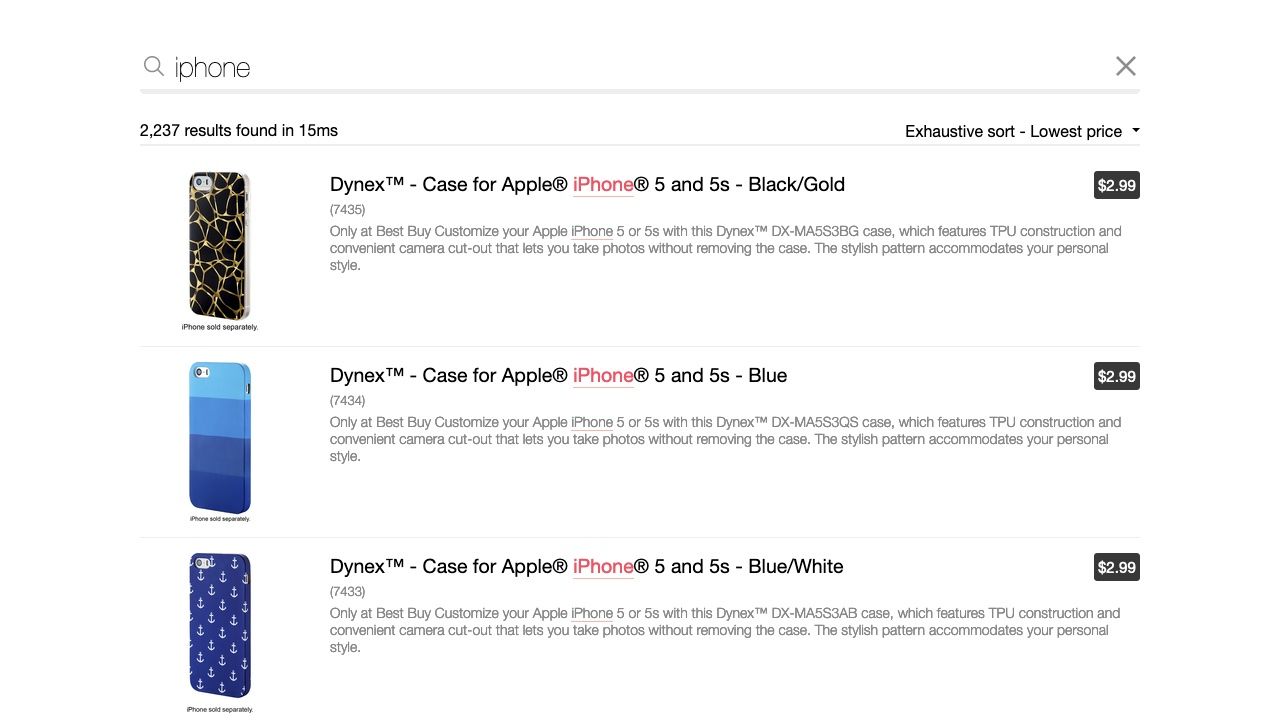
Exhaustive sorting returns and sorts all results that match the search term “iphone”: here, a list of phone cases appear at the top of the results.
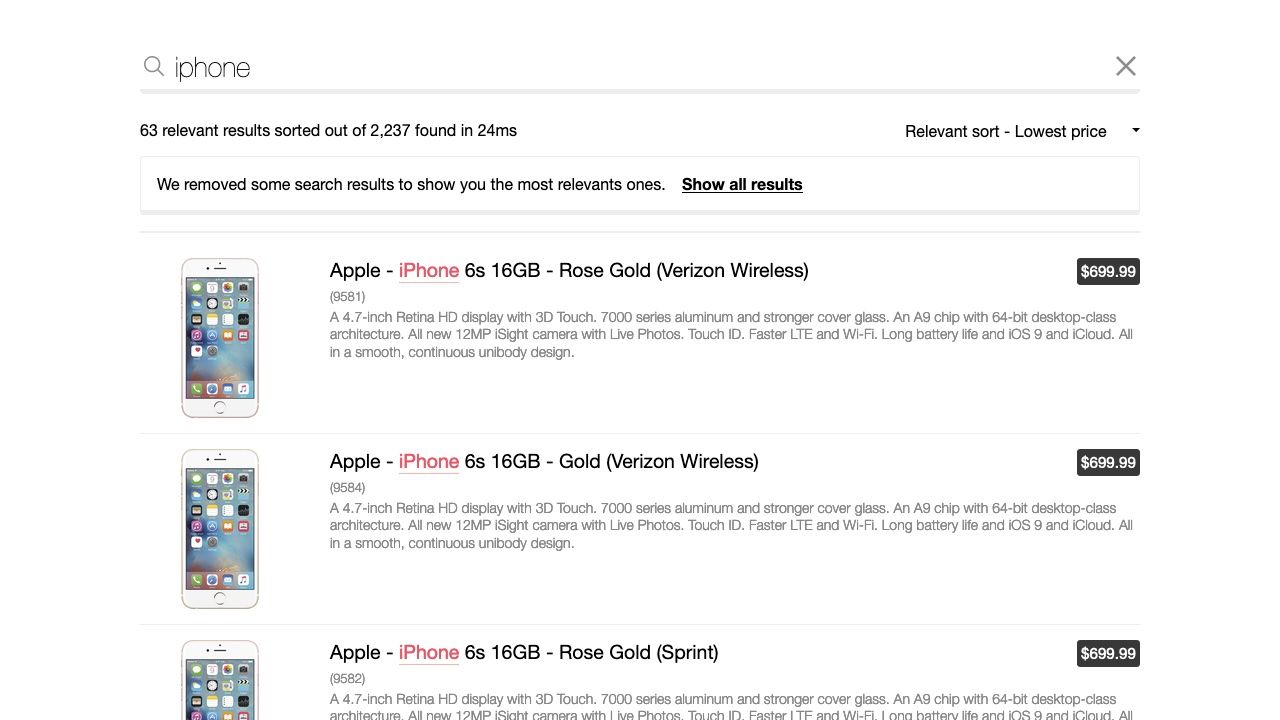
For the same search term, relevant sorting has applied a virtual replica’s custom ranking criteria to ensure that iPhone devices appear at the top of the results.
Exhaustive sorting
Relevant sorting
Effect of relevant sorting on the ranking formula
Algolia’s ranking formula isn’t overridden when you use relevant sorting. Instead, the relevant sorting algorithm:
- Selects results using the primary index’s ranking formula.
- Selects the most relevant results. You can determine how strict this should be by adjusting
relevancyStrictnesson a virtual replica. - Orders the selected results according to the virtual replica’s
customRankingcriteria. - Returns the relevant results.
The ranking formula determines which results are most relevant to the search query, but custom ranking determines the order of results. This means that parameters that affect the ranking formula, such as optionalFilters, don’t affect result ordering.
If multiple results have the same value for a sorting attribute, the other sorting attributes are used to decide which one comes first. For example, if you sort according to price and then popularity, and three results have the same cost, the engine will prioritize them according to their popularity score.
Relevant sorting considerations
Relevant sorting interacts with other features in ways you might not expect.
Caution: other re-ranking features can affect results
Other re-ranking features, such as Rules, apply after relevant sorting and will modify sort order. For example, if Personalization promotes expensive items for a particular user based on their past actions, that user might see expensive items at the top of the results, even if they’ve chosen to relevant sort from lowest to highest price.
To ensure predictable behavior, don’t use the following features or parameters with relevant sorting:
Facets count
When relevant sorting is enabled, the engine still computes facets on all results, not just those defined by the relevant sort. A UI banner detailing the behavior of the relevant sort may help manage the user’s expectations.
Enabling relevant sorting reduces the number of results
Essentially, that’s the point: it gives users more relevant results, not all results (exhaustive sorting).
For example, you search for “chromebook” on an ecommerce site and get Chromebook computers at the top of your results (so far, so good).
However, if you then sort by ascending price (because you want a cheaper computer), the top (cheapest) listed items might be “Chromebook power adapters”. With a relevant sort, you get fewer results but only see the relevant items (computers).
Using a virtual replica even with relevancyStrictness set to 0 can’t mimic the exhaustive sorting of a standard replica because it doesn’t use the same algorithm. Be aware that a virtual replica:
- Doesn’t duplicate the data. It sorts at query time.
- Can only retrieve a maximum of 20k results, so there’s no guarantee that it will fetch the “deepest” hits.
How to configure relevant sorting
Step one - Create a virtual replica index
If you want to configure relevant sorting, you first need to create a virtual replica index for each attribute you want to sort by.
Virtual replicas provide an alternative “view” of the primary index. Virtual replicas reuse the primary’s ranking formula to return relevant results. For that reason, you can’t change the ranking on virtual replicas but can use customRanking to define the sort criteria.
Step two - Connect your UI to your index
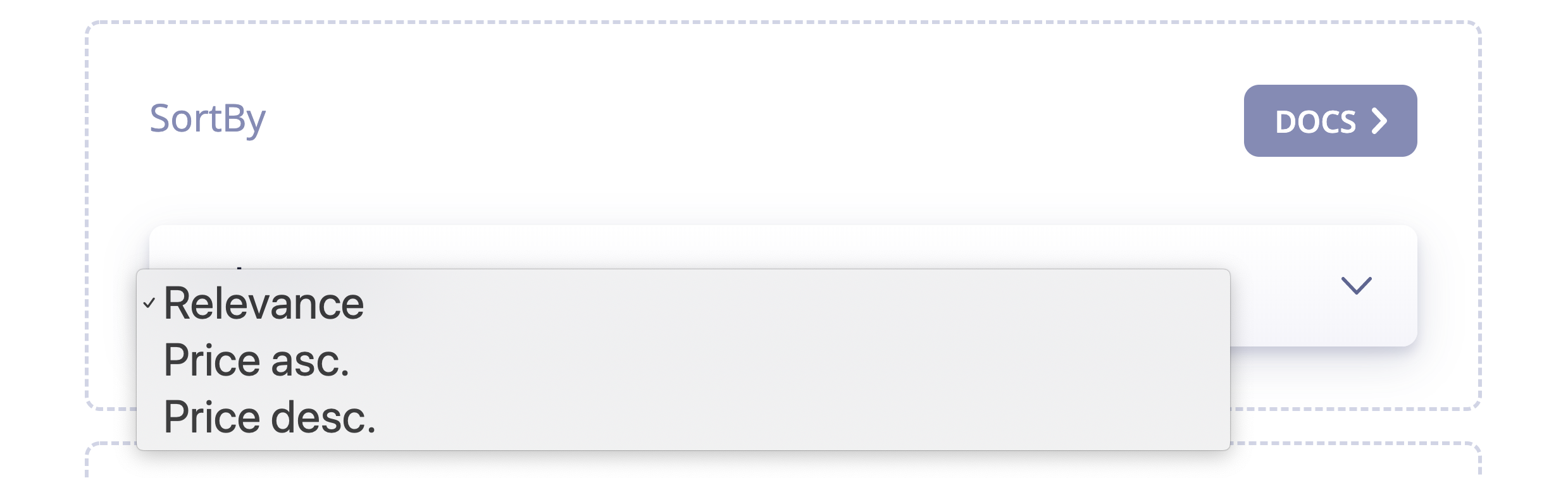
Virtual replica indices manage the backend of sorting, but you still need to implement the frontend. You can do this with either custom logic or InstantSearch.
If you’re using InstantSearch, you should use the sortBy UI widget.
To ensure the user understands how relevant sort works and ensure that they can control their experience:
- Indicate that sorting removed some results
- Offer them the option of displaying more.
You can do this with the relevantSort UI widget.